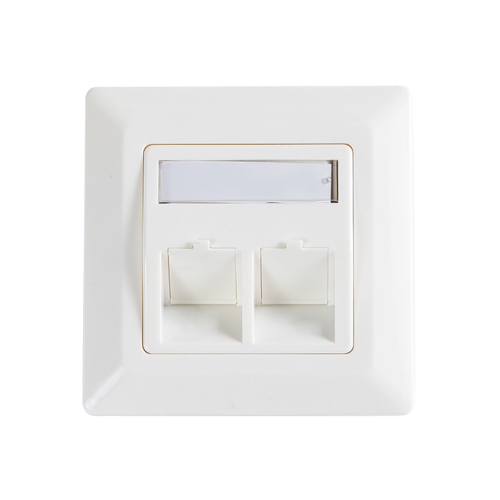
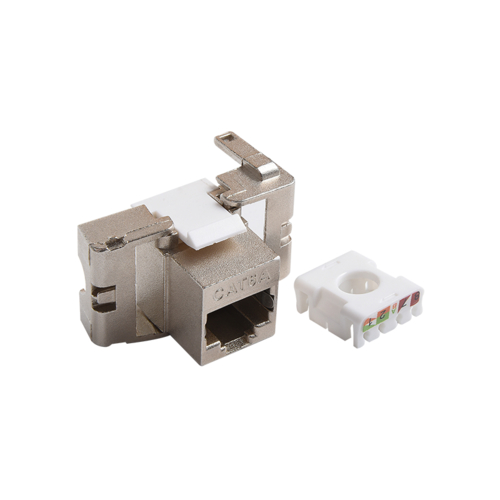
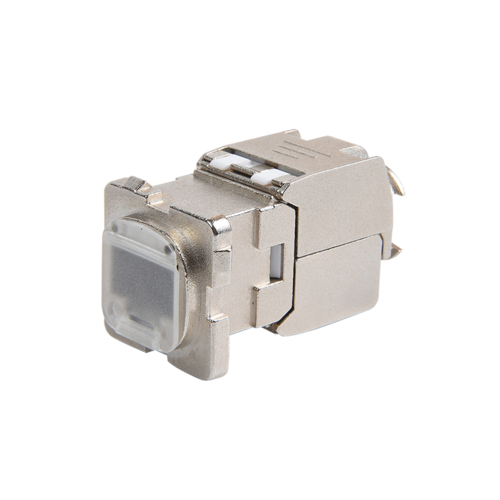
Choosing the right cable type is crucial when building an efficient and stable network cabling system. Simply put, if your environment has high electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI), such as factory workshops, hospitals, or large data centers, you should use Shielded Patch Cords; for environments with less interference, such as ordinary home networks or small and medium-sized offices, unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables are a more cost-effective and easier-to-install option.
Content
What are Shielded Patch Cords? Why are they so important?
Shielded twisted pair (STP or FTP) patch cords are network cables with one or more layers of metal shielding wrapped around the twisted pairs. This "armor" primarily serves to physically block external electromagnetic waves from entering the cable and prevent internal signals from radiating outwards.
In complex cabling environments, shielded patch cords act as data "bodyguards." Without shielding technology, strong electromagnetic fields (such as those near generators, elevator motors, or high-voltage lines) can induce noise in the cables, leading to increased error rates, data loss, and in severe cases, even network outages.
Core advantages of shielded patch cords:
- Superior anti-interference ability: Effectively resists EMI and RFI, ensuring data transmission integrity.
- Lower crosstalk: Especially in cable trays where cables are densely bundled, shielded patch cords effectively reduce signal coupling between cables (i.e., alien crosstalk ANEXT).
- Higher security: The shielding layer reduces electromagnetic radiation leakage, making it more difficult to eavesdrop on data.
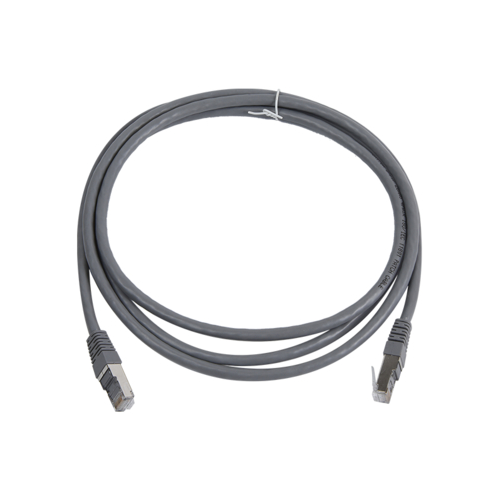

In-depth scenarios: When is it essential to choose shielded patch cords?
Not all networks need to be "fully armored," but in the following specific scenarios, deploying shielded patch cords and a matching shielded cabling system is a mandatory requirement:
- Industrial environments: Factory automation production lines are filled with large motors, welding machines, and frequency converters, which generate significant electromagnetic noise.
- Medical institutions: In hospitals, near MRI rooms and X-ray machines, high-quality shielded patch cords must be used to prevent medical equipment and network signals from interfering with each other.
- High-Density Data Centers: When hundreds or thousands of network cables are tightly bundled in server racks and operating at speeds of 10 Gigabit (10GBase-T) or higher, using Cat6A shielded patch cables effectively solves the problem of crosstalk between cables.
- Government and Confidential Organizations: For information security and leak prevention, shielded systems are the preferred choice.
When to Choose Unshielded Patch Cables (UTP)?
If your cabling environment is relatively "clean," unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables remain the mainstream choice. For most commercial office buildings, schools, and home users, UTP patch cables offer significant advantages:
- Lower Cost: The cost of cables and accompanying connectors and patch panels is usually lower than shielded systems.
- Easier Installation: They are more flexible, easier to bend and route through conduits, and do not require complex grounding procedures.
- Sufficient for Daily Needs: In the absence of strong interference sources, qualified Cat6 unshielded patch cables can fully meet the needs of Gigabit or even short-distance 10 Gigabit transmission.
Comparison Guide: Key Differences Between Shielded and Unshielded Patch Cables
- Interference Resistance: Shielded patch cables have extremely strong anti-interference performance. Thanks to the metal shielding layer, they can effectively "immunize" against external electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), making them ideal for complex electromagnetic environments. Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables rely mainly on the twisted pair structure to cancel out noise, suitable for ordinary environments.
- Grounding System Requirements: Shielded patch cables require strict grounding at both ends, while unshielded patch cables do not require grounding, simplifying setup.
- Installation Difficulty and Physical Properties: Shielded cables are thicker, stiffer, and require precise handling, while unshielded cables are thinner, flexible, and easier to install.
- Cost: Shielded patch cords are more expensive and labor-intensive to install, whereas unshielded patch cords are cheaper and easier to maintain.
- Typical Applications: Shielded patch cords are ideal for high-interference environments such as industrial automation, large data centers, medical imaging rooms, and airports. Unshielded patch cords suit everyday scenarios like home networks, small and medium offices, and schools.
The correct cabling choice is the first step to stable network operation. Before purchasing, evaluate your on-site electromagnetic environment to ensure that shielded patch cords are used where they are most needed.



 Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский